- Air Photo Server for Mac OS X Leopard v.1.0 Air Photo Server is the free server component, companion to Air Photo on iPhone or iPod Touch. It enables direct wireless printing from iPhone over local wifi network.
- SolarWinds Kiwi Syslog Server. The Kiwi Syslog Server installs on Windows and Windows Server.
- Free Syslog Server For Mac Os X 10 10 Yosemite Download
- Reading Syslog
- Free Syslog Server For Mac Os X Latest
From Splunk Wiki
Download Syslog Server Mac Software. VShell Server for UNIX v.3.5 VShell SSH2 server is a secure alternative to Telnet and FTP on Windows and UNIX providing strong encryption, robust authentication and data integrity. Fine-tune your environment with precision control and a selection of authentication methods. The demo shows an iRAP client on windows machine, so it means a iRAPP rdp server will be installed on mac and that can be access through any of rdp client or through iRAP client only @Scott Walter – prateeak ojha.
This tutorial shows how to configure Mac OS X to forward syslog events to a remote server.
The following configuration steps were tested and validated on a MacBook Pro running Mac OS X 10.6.2 (Snow Leopard).
Using the Console on Mac OS X El Capitan v10.11 and earlier. Open the Console application (from the Utilities folder inside your Applications folder). It should open to All Messages, showing the log entries for everything that’s happened recently on your Mac. Sign up now and receive a link to download Splunk Enterprise for free, and start collecting, analyzing and acting upon the untapped value of big data. I've tried to configure my OSX Splunk server so it will accept data from the syslog deamon. I've edited the /etc/syslog.conf file and added '. (Where x.x.x.x is the IP of my machine where Splunk should be listening).
Background
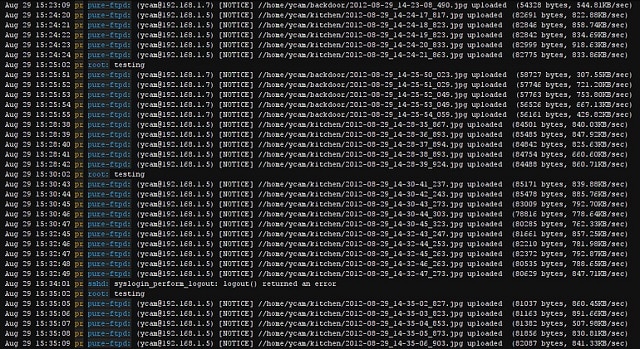
Mac OS X Console.app (Applications - Utilities - Console.app) is the standard interface to visualize all events registered by the operating system. It is simple yet functional, but not very friendly on displaying the entries and actually finding some useful information.
Splunk has a Mac OS X version that allows for a better and more complete monitoring of the system and syslog events, it can also be installed and configured as a forwarder to your central monitoring server. But it doesn’t need to be installed for just monitoring syslog generated events.
It is worth mentioning that in order to capture events forwarded by Mac OS X (or any other syslog forwarder, actually) you have to configure the Splunk server to:
(a.) receive data inputs on UDP port 514, and
(b.) allow incoming traffic through this port on all firewalls in place between the Mac OS X and the Splunk server - including the Windows Firewall, if that’s the case.
Its also worth noting that Mac OS X will simple forward all syslog data as a single source, not separating data by log file like the Universal Forwarder does.
Configuring the Mac OS X Syslogd
The next steps are to be executed in a Terminal window, the Mac OS X command line interface. The steps to configure the syslog forwarding are:
1. Open a Terminal window:Applications - Utilities - Terminal, or by using the Spotlight (shortcut: command+space > Terminal)
2. Before touching anything, make a backup copy of the syslog configuration file (syslogd.conf) into the /tmp folder:
3. Open the configuration file on your favorite editor (in this case, we’re using vi):
Use the ’sudo’ command to execute vi with ‘root’ privileges, otherwise you won’t be able to edit the file. Enter the password for the administrator account you are currently logged in as to continue.

Syslog Server For Mac Os Xp
4. Insert the following line anywhere in your syslogd.conf file, replacing the IP address 192.168.1.12 with the IP address of your Splunk server’s network interface.
Type ‘i’ in vi to enter the insert mode (text entry), then add the line above anywhere in the file.
‘’’IMPORTANT:’’’ The selector and action fields (see below) are separated by TABs. Do not use spaces.
The syslogd.conf file consists of lines with two fields: the selector field which specifies the types of messages and priorities to which the line applies, and an action field which specifies the action to be taken if a message syslogd receives matches the selection criteria.
If you would like to forward your syslog output on a different port to the standard 514, you can do this by specifying a specific port for your destination; e.g.
results in your syslog data being forwarded to port 5140 instead of the usual port 514.
The Selectors function are encoded as a Facility.Level. The line above is basically telling the Mac OS X syslog daemon to forward a copy of all (*.*) events to the syslog server listening on the IP address 192.168.1.12. If you don’t want to send all events, you can filter them out by setting a different level - for instance, you can replace the ‘*.*’ with ‘*.notice’. Check out the syslogd.conf and the syslog manual pages for all the options.
5. Save and Exit:Press ‘ESC’ to exit insert mode, and save the file by typing ’:wq <enter>’.If you don’t want to save it now, type ’:q!‘ to exit vi without saving and start over.
6. Restart the ‘syslogd’ service:But before doing so, check if it’s running by typing:
The following commands restart the service. Enter your password one more time if necessary.
Check if the service was really shut down and restarted by typing the same command again. The counter should have been reset and the PID (5070 in the example above) should be a different one.
Free Syslog Server For Mac Os X 10 10 Yosemite Download
Done.
You can use ’tcpdump’ to verify that the events are being forwarded to the remote server. Use the command ’ifconfig’ to get the name of the Mac OS X network interface connected to the same IP network segment of the Splunk server and use it as a filter for ’tcpdump’. In this case, the interface name is ‘en1’:
To log an event - open a new Terminal window on Mac OS X and use the ’logger’ command.
If tcpdump doesn't report the Testing message, first double check the tcpdump arguments then review the configuration and check if there is connectivity between the Mac OS X station and the Splunk server.
Lastly, check that UDP/514 traffic is allowed through any firewalls.
Worst case, restore your backup copy from the /tmp folder and repeat the process.
Syslog Server For Mac Os X 10.13
I’ve never seen this before but could find my way around configuring ASL logging very quickly, because a lot of things are quite intuitive:
We configure file permissions, format and rotation rules for system.log file and then define filters for the messages that we want it that log file: they must be kernel messages, have specific facilities (kinds of messages) and log level (notice).
I think I’ll do another post on ASL soon enough, explaining this in more detail.
Comparing ASL to syslog and rsyslog
I would say ASL has a really cool and very readable approach to configuring logging needs. It’s superiour to traditional syslog format.
rsyslog, which I’m finding in most Linux distros these days, is safe: it has a new syntax for configuration files that is just as easy and just as meaningful. So while ASL is clearly better than old syslog, it’s quite comparable to newer rsyslog when it comes to both functionality and configuration language.
See Also
- brew command not found - use brew for installing software
Reading Syslog
