We design Mac hardware and software with advanced technologies that work together to run apps more securely, protect your data, and help keep you safe on the web. And with macOS Big Sur available as a free upgrade, it’s easy to get the most secure version of macOS for your Mac.*
AutoKrypt for Mac OS X v.9.09 AutoKrypt is an encryption software designed for automation that will automatically encrypt or decrypt files and folders. AutoKrypt's encryption methods include password based, public and private key, secret key, OpenPGP password, OpenPGP public and.; The Lemur Project v.5.1 The Lemur Project develops search engines, browser toolbars, text analysis tools,. Free download PGP PGP for Mac OS X. PGP® Whole Disk Encryption from Symantec provides organizations with comprehensive, high performance full disk encryption for all data (user files, swap files, system files, hidden files, etc. Nov 21, 2020 Free download PGP PGP for Mac OS X. PGP® Whole Disk Encryption from Symantec provides organizations with comprehensive, high performance full disk encryption for all data (user files, swap files, system files, hidden files, etc. Out of all the Encryption Software, FileVault 2 Considered as the best one for the Mac OS systems. Jan 29, 2020 Concealer is a file encryption program specifically for Apple Mac computers. Rather than encrypt all files on your harddrive, instead it provides an encrypted area for you to drag files into.
Apple M1 chip.
A shared architecture for security.
The Apple M1 chip with built-in Secure Enclave brings the same powerful security capabilities of iPhone to Mac — protecting your login password, automatically encrypting your data, and powering file-level encryption so you stay safe. And the Apple M1 chip keeps macOS secure while it’s running, just as iOS has protected iPhone for years.
Apple helps you keep your Mac secure with software updates.
The best way to keep your Mac secure is to run the latest software. When new updates are available, macOS sends you a notification — or you can opt in to have updates installed automatically when your Mac is not in use. macOS checks for new updates every day and starts applying them in the background, so it’s easier and faster than ever to always have the latest and safest version.
Protection starts at the core.
The technically sophisticated runtime protections in macOS work at the very core of your Mac to keep your system safe from malware. This starts with state-of-the-art antivirus software built in to block and remove malware. Technologies like XD (execute disable), ASLR (address space layout randomization), and SIP (system integrity protection) make it difficult for malware to do harm, and they ensure that processes with root permission cannot change critical system files.
Download apps safely from the Mac App Store. And the internet.
Now apps from both the App Store and the internet can be installed worry-free. App Review makes sure each app in the App Store is reviewed before it’s accepted. Gatekeeper on your Mac ensures that all apps from the internet have already been checked by Apple for known malicious code — before you run them the first time. If there’s ever a problem with an app, Apple can quickly stop new installations and even block the app from launching again.
Stay in control of what data apps can access.
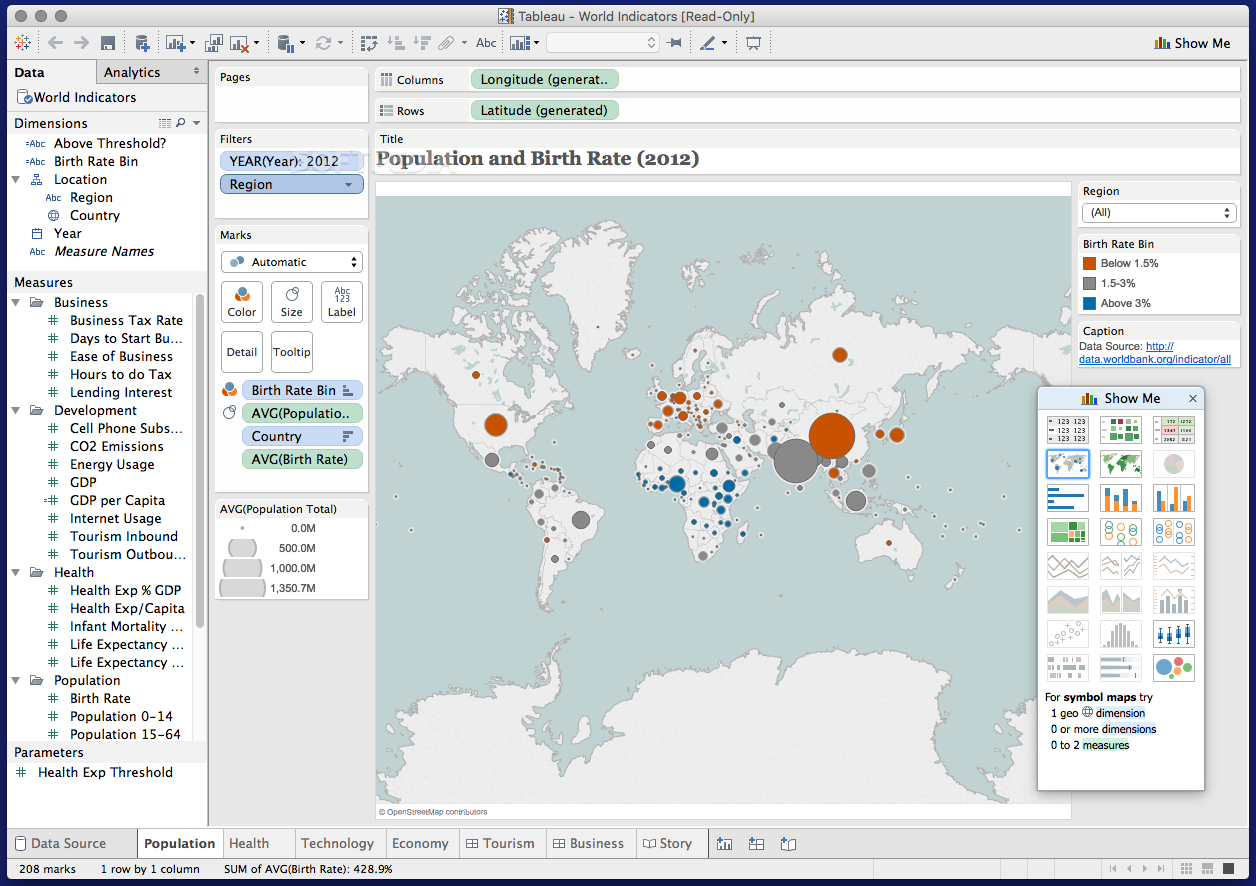
Apps need your permission to access files in your Documents, Downloads, and Desktop folders as well as in iCloud Drive and external volumes. And you’ll be prompted before any app can access the camera or mic, capture keyboard activity, or take a photo or video of your screen.
FileVault 2 encrypts your data.
With FileVault 2, your data is safe and secure — even if your Mac falls into the wrong hands. FileVault 2 encrypts the entire drive on your Mac, protecting your data with XTS-AES 128 encryption. Mac computers built on the Apple M1 chip take data protection even further by using dedicated hardware to protect your login password and enabling file-level encryption, which developers can take advantage of — just as on iPhone.
Designed to protect your privacy.
Online privacy isn’t just something you should hope for — it’s something you should expect. That’s why Safari comes with powerful privacy protection technology built in, including Intelligent Tracking Prevention that identifies trackers and helps prevent them from profiling or following you across the web. A new weekly Privacy Report on your start page shows how Safari protects you as you browse over time. Or click the Privacy Report button in your Safari toolbar for an instant snapshot of the cross-site trackers Safari is actively preventing on that web page.
Automatic protections from intruders.
Safari uses iCloud Keychain to securely store your passwords across all your devices. If it ever detects a security concern, Password Monitoring will alert you. Safari also prevents suspicious websites from loading and warns you if they’re detected. And because it runs web pages in separate processes, any harmful code is confined to a single browser tab and can’t crash the whole browser or access your data.
Find your missing Mac with Find My.
The Find My app can help you locate a missing Mac — even if it’s offline or sleeping — by sending out Bluetooth signals that can be detected by nearby Apple devices. These devices then relay the detected location of your Mac to iCloud so you can locate it. It’s all anonymous and encrypted end-to-end so no one — including Apple — knows the identity of any reporting device or the location of your Mac. And it all happens silently using tiny bits of data that piggyback on existing network traffic. So there’s no need to worry about your battery life, your data usage, or your privacy being compromised.
Keep your Mac safe.
Even if it’s in the wrong hands.
All Mac systems built on the Apple M1 chip or with the Apple T2 Security Chip support Activation Lock, just like your iPhone or iPad. So if your Mac is ever misplaced or lost, the only person who can erase and reactivate it is you.
macOS Security
I forgot my password – is there any way ('backdoor') to recover the files from my VeraCrypt volume?
Is there a 'Quick Start Guide' or some tutorial for beginners?
Can I encrypt a partition/drive where Windows is installed?
Can I directly play a video (.avi, .mpg, etc.) stored on a VeraCrypt volume?
The same goes for video recording: Before a chunk of a video file is written to a VeraCrypt volume, VeraCrypt encrypts it in RAM and then writes it to the disk. This process is called on-the-fly encryption/decryption and it works for all file types (not only for video files).
Is it possible to donate to the VeraCrypt project?
Why is VeraCrypt open-source? What are the advantages?
Remark: A similar problem also affects cryptographic hardware (for example, a self-encrypting storage device). It is very difficult to reverse-engineer it to verify that it does not contain any security flaw or secret 'backdoor'.
VeraCrypt is open-source, but has anybody actually reviewed the source code?
As VeraCrypt is open-source software, independent researchers can verify that the source code does not contain any security flaw or secret 'backdoor'. Can they also verify that the official executable files were built from the published source code and contain no additional code?
- Encrypt the entire USB flash drive. However, you will not be able run VeraCrypt from the USB flash drive.
Note: Windows does not support multiple partitions on USB flash drives. - Create a VeraCrypt file container on the USB flash drive (for information on how to do so, see the chapter Beginner's Tutorial, in the VeraCrypt User Guide). If you leave enough space on the USB flash drive (choose an appropriate size for the VeraCrypt container), you will also be able to store VeraCrypt on the USB flash drive (along with the container – not in the container) and you will be able to run VeraCrypt from the USB flash drive (see also the chapter Portable Mode in the VeraCrypt User Guide).
Does VeraCrypt also encrypt file names and folder names?
Can data be read from and written to an encrypted volume/drive as fast as if the drive was not encrypted?

Does VeraCrypt support hardware-accelerated encryption?
Is it possible to boot Windows installed in a hidden VeraCrypt volume?
Will I be able to mount my VeraCrypt volume (container) on any computer?
Can I unplug or turn off a hot-plug device (for example, a USB flash drive or USB hard drive) when there is a mounted VeraCrypt volume on it?
Will I be able to mount my VeraCrypt partition/container after I reinstall or upgrade the operating system?
Note: If the system partition/drive is encrypted and you want to reinstall or upgrade Windows, you need to decrypt it first (select System > Permanently Decrypt System Partition/Drive). However, a running operating system can be updated (security patches, service packs, etc.) without any problems even when the system partition/drive is encrypted.
Can I upgrade from an older version of VeraCrypt to the latest version without any problems?
Can I upgrade VeraCrypt if the system partition/drive is encrypted or do I have to decrypt it first?
I use pre-boot authentication. Can I prevent a person (adversary) that is watching me start my computer from knowing that I use VeraCrypt?
I use pre-boot authentication. Can I configure the VeraCrypt Boot Loader to display only a fake error message?
Can I configure VeraCrypt to mount automatically whenever Windows starts a non-system VeraCrypt volume that uses the same password as my system partition/drive (i.e. my pre-boot authentication password)?
- Mount the volume (to the drive letter to which you want it to be mounted every time).
- Right-click the mounted volume in the drive list in the main VeraCrypt window and select 'Add to System Favorites'.
- The System Favorites Organizer window should appear now. In this window, enable the option 'Mount system favorite volumes when Windows starts' and click OK.
Can a volume be automatically mounted whenever I log on to Windows?
- Mount the volume (to the drive letter to which you want it to be mounted every time).
- Right-click the mounted volume in the drive list in the main VeraCrypt window and select 'Add to Favorites'.
- The Favorites Organizer window should appear now. In this window, enable the option 'Mount selected volume upon logon' and click OK.
Alternatively, if the volumes are partition/device-hosted and if you do not need to mount them to particular drive letters every time, you can follow these steps:

- Select Settings > Preferences. The Preferences window should appear now.
- In the section 'Actions to perform upon logon to Windows', enable the option 'Mount all devices-hosted VeraCrypt volumes' and click OK.
Can a volume be automatically mounted whenever its host device gets connected to the computer?
- Mount the volume (to the drive letter to which you want it to be mounted every time).
- Right-click the mounted volume in the drive list in the main VeraCrypt window and select 'Add to Favorites'.
- The Favorites Organizer window should appear now. In this window, enable the option 'Mount selected volume when its host device gets connected' and click OK.
Note: VeraCrypt will not prompt you for a password if you have enabled caching of the pre-boot authentication password (Settings > 'System Encryption') and the volume uses the same password as the system partition/drive.
Can my pre-boot authentication password be cached so that I can use it mount non-system volumes during the session?
Best Encryption Software 2017
I live in a country that violates basic human rights of its people. Is it possible to use VeraCrypt without leaving any 'traces' on unencrypted Windows?
- Create a BartPE CD and boot it. (Note: You must perform each of the following steps from within BartPE.)
- Download the VeraCrypt self-extracting package to the RAM disk (which BartPE automatically creates).
Note: If the adversary can intercept data you send or receive over the Internet and you need to prevent the adversary from knowing you downloaded VeraCrypt, consider downloading it via I2P, Tor, or a similar anonymizing network. - Verify the digital signatures of the downloaded file (see this section of the documentation for more information).
- Run the downloaded file, and select Extract (instead of Install) on the second page of the VeraCrypt Setup wizard. Extract the contents to the RAM disk.
- Run the file VeraCrypt.exe from the RAM disk.
Can I encrypt my system partition/drive if I don't have a US keyboard?
Can I save data to the decoy system partition without risking damage to the hidden system partition?
Can I use VeraCrypt on Windows if I do not have administrator privileges?
How does VeraCrypt verify that the correct password was entered?
Can I encrypt a partition/drive without losing the data currently stored on it?
- If you want to encrypt an entire system drive (which may contain multiple partitions) or a system partition (in other words, if you want to encrypt a drive or partition where Windows is installed), you can do so provided that you use VeraCrypt 5.0 or later and that you use Windows XP or a later version of Windows (such as Windows 7) (select 'System' > 'Encrypt System Partition/Drive' and then follow the instructions in the wizard).
- If you want to encrypt a non-system partition in place, you can do so provided that it contains an NTFS filesystem, that you use VeraCrypt 6.1 or later, and that you use Windows Vista or a later version of Windows (for example, Windows 7) (click 'Create Volume' > 'Encrypt a non-system partition' > 'Standard volume' > 'Select Device' > 'Encrypt partition in place' and then follow the instructions in the wizard).
Can I run VeraCrypt if I don't install it?
Some encryption programs use TPM to prevent attacks. Will VeraCrypt use it too?
If the attacker has administrator privileges, he can, for example, reset the TPM, capture the content of RAM (containing master keys) or content of files stored on mounted VeraCrypt volumes (decrypted on the fly), which can then be sent to the attacker over the Internet or saved to an unencrypted local drive (from which the attacker might be able to read it later, when he gains physical access to the computer).
If the attacker can physically access the computer hardware (and you use it after such an access), he can, for example, attach a malicious component to it (such as a hardware keystroke logger) that will capture the password, the content of RAM (containing master keys) or content of files stored on mounted VeraCrypt volumes (decrypted on the fly), which can then be sent to the attacker over the Internet or saved to an unencrypted local drive (from which the attacker might be able to read it later, when he gains physical access to the computer again).
The only thing that TPM is almost guaranteed to provide is a false sense of security (even the name itself, 'Trusted Platform Module', is misleading and creates a false sense of security). As for real security, TPM is actually redundant (and implementing redundant features is usually a way to create so-called bloatware).
For more information, please see the sections Physical Security and Malware in the documentation.
Do I have to dismount VeraCrypt volumes before shutting down or restarting Windows?
Which type of VeraCrypt volume is better – partition or file container?
What's the recommended way to back up a VeraCrypt volume?
What will happen if I format a VeraCrypt partition?
Is it possible to change the file system of an encrypted volume?
Is it possible to mount a VeraCrypt container that is stored on a CD or DVD?
Is it possible to change the password for a hidden volume?
When I use HMAC-RIPEMD-160, is the size of the header encryption key only 160 bits?
How do I burn a VeraCrypt container larger than 2 GB onto a DVD?
The DVD burning software you use should allow you to select the format of the DVD. If it does, select the UDF format (ISO format does not support files larger than 2 GB).
Can I use tools like chkdsk, Disk Defragmenter, etc. on the contents of a mounted VeraCrypt volume?
Does VeraCrypt support 64-bit versions of Windows?
Can I mount my VeraCrypt volume under Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux?
Is there a list of all operating systems that VeraCrypt supports?
Is it possible to install an application to a VeraCrypt volume and run it from there?
What will happen when a part of a VeraCrypt volume becomes corrupted?
What do I do when the encrypted filesystem on my VeraCrypt volume is corrupted?
We use VeraCrypt in a corporate/enterprise environment. Is there a way for an administrator to reset a volume password or pre-boot authentication password when a user forgets it (or loses a keyfile)?
Similarly, you can reset a pre-boot authentication password. To create a backup of the master key data (that will be stored on a VeraCrypt Rescue Disk and encrypted with your administrator password), select 'System' > 'Create Rescue Disk'. To set a user pre-boot authentication password, select 'System' > 'Change Password'. To restore your administrator password, boot the VeraCrypt Rescue Disk, select 'Repair Options' > 'Restore key data' and enter your administrator password.
Note: It is not required to burn each VeraCrypt Rescue Disk ISO image to a CD/DVD. You can maintain a central repository of ISO images for all workstations (rather than a repository of CDs/DVDs). For more information see the section Command Line Usage (option /noisocheck).
Can our commercial company use VeraCrypt free of charge?
We share a volume over a network. Is there a way to have the network share automatically restored when the system is restarted?
It is possible to access a single VeraCrypt volume simultaneously from multiple operating systems (for example, a volume shared over a network)?
Can a user access his or her VeraCrypt volume via a network?
I encrypted a non-system partition, but its original drive letter is still visible in the 'My Computer' list. When I double click this drive letter, Windows asks if I want to format the drive. Is there a way to hide or free this drive letter?
- Right-click the 'Computer' (or 'My Computer') icon on your desktop or in the Start Menu and select Manage. The 'Computer Management' window should appear.
- From the list on the left, select 'Disk Management' (within the Storage sub-tree).
- Right-click the encrypted partition/device and select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
- Click Remove.
- If Windows prompts you to confirm the action, click Yes.
When I plug in my encrypted USB flash drive, Windows asks me if I want to format it. Is there a way to prevent that?
How do I remove or undo encryption if I do not need it anymore? How do I permanently decrypt a volume?
Encryption Software Mac Os X Freeware Games
What will change when I enable the option 'Mount volumes as removable media'?
Is the online documentation available for download as a single file?
Do I have to 'wipe' free space and/or files on a VeraCrypt volume?
If you believe that an adversary will be able to decrypt the volume (for example that he will make you reveal the password), then the answer is yes. Otherwise, it is not necessary, because the volume is entirely encrypted.
How does VeraCrypt know which encryption algorithm my VeraCrypt volume has been encrypted with?
I haven't found any answer to my question in the FAQ – what should I do?